Current Control Config Attributes
These are the current control configuration attributes associated with a Motion Control Axis.
Current Vector Limit
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - D | Set | REAL | 100 FD | 0 | 10 3 | % Motor Rated |
Current Vector Limit value applied to the current vector limiter to provide a configurable limit to the magnitude of the current vector.
Kqp
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set | REAL | 0 FD | 0 | 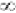 | Radians/Sec |
The Kqp attribute determines the Iq Proportional Gain value that multiplies the Iq Current Error signal. This value directly determines the bandwidth of the torque producing current loop. Iq Proportional Gain value that multiplies the Iq Current Error signal before applying it to the Iq decoupling summing junction as part of the torque producing current loop. In cases where the torque producing current loop is controlled by something other than the traditional PI regulator, the Torque Loop Bandwidth is used by the drive to provide single parametric control of the current loop bandwidth. If the Flux Loop Bandwidth is not supported, the drive will use the Torque Loop Bandwidth for tuning both the torque producing and flux producing current loops.
Kqi
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set | REAL | 0 | 0 | 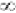 | Radians/Sec |
Iq Integral Gain value that, together with Kqp, multiplies the Iq Current Error signal before applying it to the Iq Integrator Error accumulator. The reciprocal of this value, 1/Kqi, represents the integrator time constant for the torque current loop. A value of 0 for this attribute disables the integrator.
Kdp
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set | REAL | 0 DB | 0 | 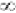 | Radians/Sec |
The Kdp attribute determines the Id Proportional Gain value that multiplies the Id Current Error signal. This value directly determines the bandwidth of the flux producing current loop.
Kdi
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set | REAL | 0 DB | 0 | 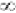 | Radians/Sec |
The Kdi attribute determines the Id Integral Gain value that, together with Kdp, multiplies the Id Current Error signal before applying it to the Id Integrator Error accumulator. The reciprocal of this value, 1/Kdi, represents the integrator time constant for the flux current loop. A value of 0 for this attribute disables the integrator.
Flux Loop Bandwidth
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set/SSV | REAL | Eq7 | 0 | 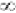 | Loop Bandwidth Units |
The Flux Loop Bandwidth attribute determines the Id Proportional Gain value that multiplies the Id Current Error signal before applying it to the Iq decoupling summing junction as part of the flux producing current loop. In cases where the flux producing current loop is controlled by something other than the traditional PI regulator, the Flux Loop Bandwidth is used by the drive to provide single parametric control of the current loop bandwidth. If the Flux Loop Bandwidth is not supported, the drive shall use the Torque Loop Bandwidth for tuning both the torque producing and flux producing current loops.
Flux Integral Time Constant
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - C | Set/SSV | REAL | 0 | 0 | 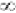 | Seconds |
The Flux Integral Time Constant value determines the response time of the flux producing current loop integrator. When used for Pole-Zero cancelation, this value is set to the electrical time constant of the motor. A value of 0 for the Flux Integral Time Constant disables the integrator.
Flux Up Control
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional- D (Induction Motor) | Set | USINT | 0 | - | - | Enumeration 0 = No Delay (R) 1 = Manual Delay (O) 2 = Automatic Delay (O) 3-255 = Reserved |
When the motion axis is enabled, DC current is applied to an induction motor to build stator flux before transitioning to the Running state. This attribute controls how an induction motor is to be fluxed in the Starting state before transitioning to the Running state. If No Delay is selected, the axis transitions immediately to the Running state while the motor flux is building. With Manual Delay, the axis remains in the Starting state for the Flux Up Time to allow time for the motor to be fully fluxed. With Automatic Delay, the drive device determines the amount of time to delay to fully flux the motor based on motor configuration attribute data or measurements.
If this attribute is not supported in the implementation, it is recommended that the drive establish induction motor flux using alternative means before transitioning to the Running state.
Flux Up Time
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - D (Induction Motor) | Set | REAL | 0 | 0 | 10 3 | Seconds |
The Flux Up Time attribute sets the amount of time the drive device allows to build full motor flux before transitioning to the Running state.
Feedback Commutation Aligned
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - CE (PM) | Set/GSV | USINT | 0 DB | - | - | Enumeration 0 = Not Aligned (R) 1 = Controller Offset (R) 2 = Motor Offset (O) 3 = Self-Sense (O) 4 = Database Offset (O) 5-255 = Reserved |
This enumerated parameter is set to Controller Offset (1) when the motor mounted absolute feedback device is to be aligned with the stator windings of the PM motor according to the Commutation Offset value. In some cases, the Commutation Offset can be preset to a value established by factory alignment of the motor feedback device relative to the motor stator windings.
A setting of Not Aligned (0) indicates that the motor is not aligned, and that the Commutation Offset value is not valid. If the Commutation Offset is not valid, it cannot be used by the drive to determine the commutation angle. Any attempt to enable the drive with an invalid commutation angle will result in a Start Inhibit condition.
Alignment can be achieved using a Commutation Test that measures and sets the Commutation Offset for the motor or by direct user entry. If this attribute is set to Motor Offset (2), the drive derives the commutation offset directly from the motor. If set to Self-Sense (3), the drive automatically measures the commutation offset when it transitions to the Starting state for the first time after a power cycle. This generally applies to a PM motor equipped with a simple incremental feedback device.
Commutation Offset
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Required - CE (PM Motor) !LTM | Set | REAL | 0 DB | 0 | 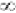 | Electrical Degrees |
The Commutation Offset attribute specifies the commutation offset of the PM motor mounted feedback device in units of electrical degrees. This attribute specifies the offset from a commutation reference position defined by applying DC current into the A terminal and out of the shorted B and C terminals of the motor and allowing the rotor to move to its magnetic null position relative to the stator. On an absolute encoder or resolver, the offset is the difference from the device’s zero absolute position and the commutation reference position. On an incremental encoder or Hall sensor with UVW signals, the offset is the difference between the position corresponding to a transition of the commutation device’s W (S3) channel with the U (S1) channel high and the V (S2) channel low, and the commutation reference position. The commutation offset is only applicable to the motor mounted Feedback 1 device.
When the optional Commutation Alignment attribute is supported and set to Controller Offset, the drive shall apply the Commutation Offset value from the controller to determine the electrical angle of the motor. In this case, a valid Commutation Offset value must be established by the controller. In the unusual case where the commutation offset is also stored in the motor and differs significantly from the Commutation Offset value from the controller, the drive shall transition to the Start Inhibited state.
If the Commutation Alignment attribute is not set to Controller Offset, the Commutation Offset value from the controller is ignored by the drive and the drive must determine its internal commutation offset value by other means. Without a valid commutation offset, the drive shall be Start Inhibited.
Commutation Self-Sensing Current
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - CE (PM Motor) | Set | REAL | 100 | 0 | 200 | % Motor Rated |
When a PM motor feedback drive device is an incremental encoder without UVW tracks for commutation, a Self-Sensing algorithm is run during the Starting state that determines the Commutation Offset to apply to the position feedback. This algorithm applies a current to the motor stator to orient the rotor to establish the motor commutation phasing.
Commutation Polarity
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - CE (PM Motor) | Set | USINT | 0 | - | - | Enumeration 0 = Normal 1 = Inverted 2-255 = Reserved |
When a PM motor is using UVW signals for commutation startup, it is critical that the UVW phases of the commutation device follow the phasing of the motor. Normal polarity implies UVW phasing according to factory specification when the commutation device is moving in the factory defined positive direction. Inverted polarity effectively switches the UVW phasing to UWV thus reversing the directional sense of the commutation device. If it is determined through a Commutation Test that the phasing of the motor and the phasing of the commutation device have opposite polarity, this attribute can be used to compensate for the mismatch.
Commutation Offset Compensation
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - CE (IPM Only) | Set | REAL | 0 | 0 | 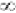 | Electrical Degrees |
This value specifies the change in the Commutation Offset value in units of electrical degrees as a linear function of current. When the Iq current is +100% of rated continuous current, the Commutation Offset value is decreased by the value of this attribute. When the Iq current is -100%, the Commutation Offset is increased by the value of the attribute. This attribute is used by the drive to compensate for changes in the optimal Commutation Offset angle that can occur as a function of motor current.
Commutation Alignment
Usage | Access | Data Type | Default | Min | Max | Semantics of Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Optional - CE (PM Motor) !LTM | Set | USINT | 0 | 0 | 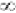 | Enumeration: 0 = Not Aligned (R) 1 = Controller Offset (R) 2 = Motor Offset (O) 3 = Self-Sense (O) 4-255 = Reserved |
This enumerated parameter is set to Controller Offset (1) when the motor mounted absolute feedback device is to be aligned with the stator windings of the PM motor according to the Commutation Offset value. In some cases, the Commutation Offset can be preset to a value established by factory alignment of the motor feedback device relative to the motor stator windings. A setting of Not Aligned (0) indicates that the motor is not aligned, and that the Commutation Offset value is not valid. If the Commutation Offset is not valid, it cannot be used by the drive to determine the commutation angle. Any attempt to enable the drive with an invalid commutation angle shall result in a Start Inhibit condition. Alignment can be achieved via a Commutation Test that measures and sets the Commutation Offset for the motor or by direct user entry. If this attribute is set to Motor Offset (2), the drive derives the commutation offset directly from the motor. If set to Self-Sense (3), the drive automatically measures the commutation offset when it transitions to the Starting state for the first time after a power cycle. This generally applies to a PM motor equipped with a simple incremental feedback device.
The Default Commutation Alignment value used for the Feedback Commutation Aligned and Commutation Alignment attributes depends on the associated Feedback Type and whether the motor commutation device is Factory Aligned. When the Motor Data Source is from Datasheet, it is assumed that the motor is not Factory Aligned. When the Motor Data Source is from Database, the motor data in the database indicates if the motor is Factory Aligned.
The following table correlates the default commutation alignment with the valid commutation alignment selections.
Default Commutation Alignment | Valid Commutation Alignment Selections | ||
Feedback Type | Factory Aligned - True | Factory Aligned - False | |
Digital AqB | - | Self-Sense* | Not Aligned | Self-Sense |
Digital AqB with UVW | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Self-Sense |
Digital Parallel | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset |
Sine/Cosine | - | Self-Sense* | Not Aligned | Self-Sense |
Sine/Cosine with UVW | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Self-Sense |
Hiperface | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset | Self-Sense |
EnDat Sine/Cosine | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset | Self-Sense |
EnDat Digital | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset |
Resolver | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset |
SSI Digital | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset |
Hiperface DSL | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset |
BiSS Digital | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset |
SSI Sine/Cosine | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Self-Sense |
SSI AqB | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Self-Sense |
BiSS Sine/Cosine | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Self-Sense |
Tamagawa Serial | Motor Offset* | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset |
Nikon Serial | Motor Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset | Motor Offset |
Stahl SSI | Database Offset | Not Aligned | Not Aligned | Database Offset | Controller Offset |
Track Section | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Track Mover | N/A | N/A | N/A |
* If the drive does not support the optional Commutation Alignment enumerations Self-Sense and Motor Offset, the create time default Commutation Alignment of Not Aligned is retained. | |||
Provide Feedback
