- Studio 5000 Logix Designer
- Tasks, programs, and routines
- Add-On Instructions
- Controller Organizer
- Logical Organizer
- Alarms
- Tag-based alarms
- Tag Editor and Data Monitor
- Configure settings for Tag Editor and Data Monitor
- Equipment phases
- Equipment Sequences
- Equipment Sequence Diagrams
- Ladder Editor
- Structured Text Editor
- Sequential Function Chart Editor
- Define the steps of an SFC process
- PlantPAx instruction properties
- Controller Properties
- Editing Controller Properties
- Controller Security
- Source Protection
- License Source Protection for Routines and Add-On Instructions
- Module Information
- 1756 ControlLogix I/O Modules
- Instruction Set
Safely-Limited Position (SLP)
This instruction only applies to the
Compact GuardLogix
5380 and GuardLogix
5580 controllers.The Safely-Limited Position (SLP) instruction monitors the position of a motor or axis to ensure that the position does not deviate above or below defined limits.
Available Languages
Ladder Diagram

Function Block
This instruction is not available in function block.
Structured Text
This instruction is not available in structured text.
Safely-Limited Position Application
Safely-Limited Position is used with a CIP safety drive that supplies speed of a motor or axis and a Safe Feedback Interface (SFX) instruction to scale the feedback. During operation, the SLP instruction sets the limit output when the motor position moves outside of the specified limits. During operation of the SLP function the limits may be adjusted. The output is used to initiate an application specific action such as STO, SS1, SS2 or STO.
Operands
IMPORTANT:
Unexpected operation may occur if:
- Output tag operands are overwritten
- Members of a structure operand are overwritten
- Structure operands are shared by multiple instructions
- The rung in condition is no longer true
- An instruction fault has occurred
WARNING:
The SLP Safety Control structure contains internal state information. If any of the configuration operands are changed while in run mode, accept the pending edits and cycle the controller mode from Program to Run for the changes to take effect.
The following table provides operands used for configuring the instruction.
Operand | Data Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Safety Control | SAFELY_LIMITED_POSITION | tag | Data structure required for proper operation of instruction. |
Restart Type | list item | This input selects the Restart Type for the instruction. MANUAL (0) A 0 to 1 transition of the Reset input is required after Request has been removed to enable the instruction to operate. AUTOMATIC (1) The instruction will reset when the Request has been removed and no fault is present [FP] = OFF(0). Once reset, the instruction will be able to operate.  ATTENTION: Only use Automatic Restart in applications where it is determined that no unsafe conditions occur from its use. | |
Cold Start Type | list item | Selects the Behavior when applying controller power or a controller mode change to Run. MANUAL (0) A 0 to 1 transition of the Reset input is required with the Request removed to enable the instruction to operate. AUTOMATIC (1) The instruction resets when the Request has been removed. | |
Check Delay | INT | immediate tag | This operand defines the delay time between the SLP function request and the start of position monitoring. Range: 0 to 32767 Units: mSec |
The following table explains the instruction inputs.
Operand | Data Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Positive Travel Limit | REAL | immediate tag | This operand sets the maximum position allowed before the SLP Limit Output is set. A change in this value takes effect immediately when the function is operating. For linear motion (SFX Unwind = 0) Range: REAL For rotary motion application (SFX Unwind  0) 0)Range: Negative Travel Limit to (Unwind/Position Scaling) Units: Position Units |
Negative Travel Limit | REAL | immediate tag | This operand sets the maximum position allowed before the SLP Limit Output is set. A change in this value takes effect immediately when the function is operating. For linear motion (SFX Unwind = 0) Range: REAL For rotary motion application (SFX Unwind  0) 0)Range: 0 to Positive Travel Limit Units: Position Units |
Feedback SFX | SAFETY_FEEDBACK_INTERFACE | tag | This operand provides position data. Assign this operand is to the Safety Control tag of the SFX instruction that is used with this SLP instruction. The following members of the SFX Safety Control tag are used: FeedbackSFX.ActualPosition Units: Feedback Counts FeedbackSFX.PositionScalingOut Units: Feedback Counts / Position Unit FeedbackSFX.UnwindOut Units: Counts / Cycle FeedbackSFX.ActualCycles Units: Cycles |
Request | BOOL | tag | This operand enables the SLP function to operate. ON(1): allows SLP function to begin monitoring. OFF(0): allows function reset according to Restart Type |
Reset 1 | BOOL | tag | This operand resets the SLP function. An OFF(0) to ON(1) transition resets the SLP function and Fault Present (FP) provided the Request is OFF(0) and any fault condition has been removed. The Request Required (RR) output indicates when a reset is required to reset the instruction. |
1
ISO 13849-1 stipulates instruction reset function must occur on falling edge signals. To comply with ISO 13849-1 requirements, add the logic immediately before this instruction. Rename the ‘Reset Signal’ tag in this example to the reset signal tag name. Then use the OSF instruction Output Bit tag as the instruction’s reset source.
This table explains instruction outputs. The outputs are external tags (safety output modules) or internal tags used in other logic routines.
Operand | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Output 1 [O1] | BOOL | ON(1): Indicates the instruction is executing and the function is not faulted. OFF(0): Any of these conditions: |
Reset Required [RR] | BOOL | ON(1): Indicates that a Reset is required to restart the SLP function instruction and or to clear faults. See Reset Input for Reset sequence. OFF(0): Normal operation under Automatic Restart operation. |
Fault Present [FP] | BOOL | ON(1): A fault is present in the instruction. OFF(0): The instruction is operating normally. |
Diagnostic Code | SINT | This output indicates the diagnostic status of the instruction. See Diagnostic Codes and Corrective Actions for specific codes and actions. |
Fault Type | SINT | This output indicates the type of fault that occurred. See the Fault Codes and Corrective Actions section for specific codes and actions. |
Check Delay Active | BOOL | ON(1): Indicates that Check Delay timer is active. |
This table explains instruction outputs that are written to the user-specified tag.
Operand | Data Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
SLP Active | BOOL | tag | The SLP instruction writes the SLP Active status to this tag. OFF(0): SLP not active ON(1): SLP active Tip: Assign the SLP Active operand to the SLP Active member of the safety output tag structure corresponding to the motion safety instance of the drive module. The corresponding Axis Safety Status updates automatically in the drive axis tag structure to enable coordination of the motion task with the safety task. |
SLP Limit | BOOL | tag | The SLP instruction writes the SLP Limit status to this tag. OFF(0): Position has not reached the limit ON(1): The position limit was reached or exceeded Tip: Assign the SLP Limit operand to the SLP Limit member of the safety output tag structure corresponding to the motion safety instance of the drive module. The corresponding Axis Safety Status updates automatically in the drive axis tag structure to enable coordination of the motion task with the safety task. |
SLP Fault | BOOL | tag | The SLP instruction writes the SLP Fault status to this tag. OFF(0): Not faulted ON(1): Faulted SLP Fault bit to be set to ON (1) state for the following fault type and corresponding condition:
An instruction input operand value is out of range.
SLP requires that a home position be defined in the SFX instruction.
The feedback used for monitoring is not valid or the SFX instruction is not running when SLP is requested. Tip: Assign the SLP Fault operand to the SLP Fault member of the safety output tag structure corresponding to the motion safety instance of the drive module. The corresponding Axis Safety Faults tag updates automatically in the drive axis tag structure to enable coordination of the motion task with the safety task. |
IMPORTANT:
Do not write to any instruction output tag under any circumstances.
Affects Math Status Flags
No
Major/Minor Faults
None specific to this instruction. See Index Through Arrays for array-indexing faults.
Execution
Ladder Diagram
Condition/State | Action Taken |
|---|---|
Prescan | The .01, .FP, .RR, .SLPActive, .SLPLimit, .SLPFault, and .CheckDelayActive outputs are cleared to OFF(0). The Diagnostic Code output is set to 0. The Fault Type output is set to 1 |
Rung-condition-in is false | The .O1, .SLPActive, .SLPLimit and .CheckDelayActive outputs are cleared to OFF(0). If an instruction fault is present when rung went false the fault condition will be maintained and Diagnostic Code displayed. |
Rung-condition-in is true | The instruction executes. |
Postscan | N/A |
Operation
Normal Operation
The SLP function begins if it has been previously reset and the Request input is asserted ON(1). At this point the Check Delay Timer begins. When the Check Delay Timer expires, position monitoring begins. The Actual Position, provided by an SFX instruction, is compared to the Positive and Negative Position Limits. If the position is not within these limits then the Limit Output is set to ON(1) and remains set until the SLP function is reset. The SFX instruction must be homed before the SLP function operates.
Position values used in the SLP instruction are in Position Units. A position unit is user defined according to the particular application and is configured in the SFX instruction.
During operation the Position Limits may be programmatically changed. If the limits are changed while the function is operating then the new limits will take effect immediately.
Pass-Through Tags
A Safe Motion Monitoring Drive has one or more motion axes that are controlled by a motion task. The Safe Motion Monitoring Drive also has one or more motion safety instances that support safety functions used in a safety task of a safety controller. Some of the tags associated with a drives motion safety instance are pass-through tags. The following table shows the pass-through tags and the corresponding axis tags for the SLP function:
SLP Instruction Output | Pass-Through Tags for Motion Safety Instances | Safe Motion Monitoring Drive Action | Axis Tag |
|---|---|---|---|
SLP Active | module 1 :SO.SLPActive[instance2 ] | updates tag | axis 3 .SLPActiveStatus |
SLP Limit | module 1 :SO.SLPLimit[instance2 ] | updates tag | axis 3 .SLPLimitStatus |
SLP Fault | module 1 :SO.SLPFault[instance2 ] | updates tag | axis 3 .SLPFault |
1
module is the name for the drive module in Logix Designer I/O Configuration tree2
instance is 1 or 2 for dual axis drives otherwise null3
axis is the axis name in the Logix Designer Motion Group and is associated with module When assigning the SLP Active, SLP Limit and SLP Fault instruction outputs to the motion safety instance pass-through tags, the corresponding Axis Safety Status and Axis Safety Faults tags automatically update in the motion controller. The motion control task of motion controller reads the Axis Safety Status and the Axis Safety Faults tags to coordinate operation between the safety task and motion task. The following is a typical sequence of events:
- The safety application receives an input to begin speed position monitoring.
- The safety application sets the Request input ON(1) to request the SLP function.
- The SLP instruction sets SLP Active output and writes the module:SO.SLPActive[instance] tag of the motion safety instance of the drive.
- The motion safety instance in the drive updates the Axis Safety Status tag read in the motion controller.
- The motion application controls the axis position to keep within the SLP Travel Limits.
In many applications it is necessary for the SLP Positive Travel Limit or Negative Travel Limit to change dynamically. Changes to the SLP Travel Limits are range checked and then applied to the SLP function even if the function is active. It may also be necessary for the motion application to coordinate speed control with Active Limit changes. To accommodate motion coordination the safety controller tag list contains two general purpose 16 bit tags for each motion safety instance. These tags appear as module:SO.PassThruData[A|B][instance]. Axis tags named axis.AxisSafetyDataA and axis.AxisSafetyDataB are updated whenever the corresponding pass-through tags module:SO.PassThruDataA[instance] and module:SO.PassThruDataB[instance] change values.
Normal Operation, Automatic Restart
The following diagram shows normal operation with Automatic Restart. After Check Delay expires the Position is shown to be within the Positive and Negative Travel Limits. The diagram then shows the position moving outside of the limits and the Limit Output is set to ON(1). For automatic restart operation, the SLP function is reset when the Request is removed, OFF(0), provided no SLP faults have occurred.

Normal Operation, Manual Restart
When manual restart is enabled, the SLP function requires a reset before subsequent operation. The Reset output indicates that the Reset input must make an OFF(0) to ON(1) transition to reset the function after the Request input is removed OFF(0). The following diagram shows normal operation with manual restart.

Faulted Operation
Faults for SLP may be for invalid configuration, SFX Instruction not ready or not homed as described in the Fault Codes and Corrective Actions section.
Fault Codes and Corrective Actions
Fault Code | Description | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
1 | No Fault | None. |
2 | Invalid Configuration Fault | Check the Positive and Negative Travel limits. For Rotary motion, these values must be less than (unwind * position scaling) and the positive limit must be greater than the negative limit. After the configuration is correct then reset the fault. |
101 | Axis Not Homed Fault | The SFX instruction used with SLP must be homed. SLP only works with absolute positions. Home the SFX instruction used with this SLP instruction. |
102 | SFX Instruction Not Ready | Ensure that the SFX function that supplies inputs to this SLP instance is executing and not faulted before requesting SLP. |
Diagnostic Codes and Corrective Actions
Diagnostic Code | Description | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
0 | No diagnostic information. | None |
10 | Rung went false while SLP function was executing. | Make sure this instruction is enabled. |
20 | Positive Travel Limit value not valid | If unwind is  0 then the Limit value must be less than (Unwind/Position Scaling). 0 then the Limit value must be less than (Unwind/Position Scaling).The Positive Travel Limit must be  Negative Travel Limit. Negative Travel Limit. |
21 | Negative Travel Limit value not valid. | The Negative Travel Limit must be less than the Positive Travel Limit. |
22 | Check Delay value not valid | Check the Check Delay value to ensure it is  0 and 0 and 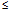 32767. 32767. |
23 | Positive Travel Limit exceeded | Move the axis to a lower position. |
24 | Negative Travel Limit exceeded | Move the axis to a larger position. |
Example

Provide Feedback
