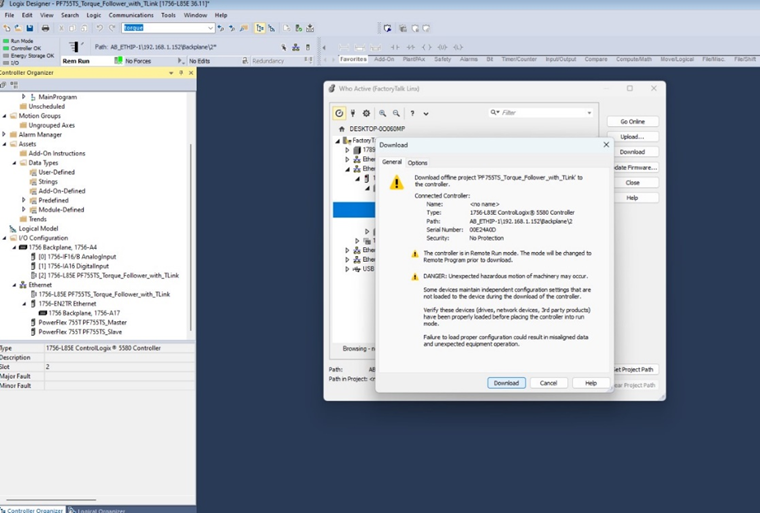
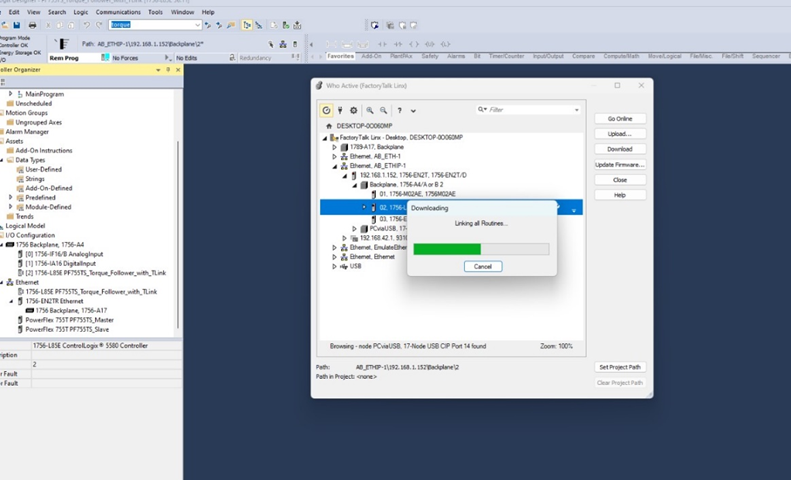
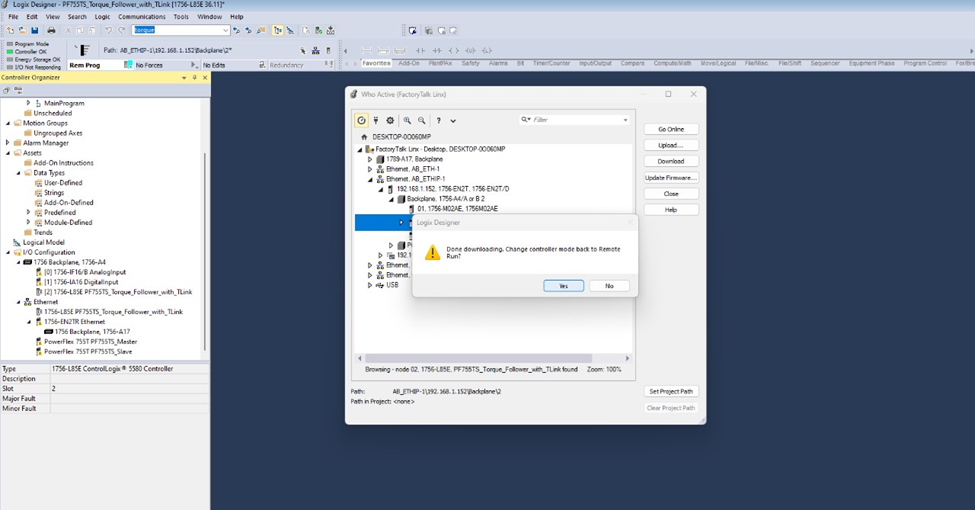
Downloads
What is this for?
The purpose of this document is to provide guidelines how to setup a load sharing application using a torque follower setup.
Load sharing is a term used to describe a system where multiple drives and motors are coupled and used to run one mechanical load.
The following assumptions are made:
- Drives and motors are properly sized for the application
- The drives are at factory default settings
- The motors are equipped with rugged feedback devices
- Drives are equipped with TLink option module and feedback cards
Need Help?
If you need help with an application or have feedback from the Innovation Center, please contact us.
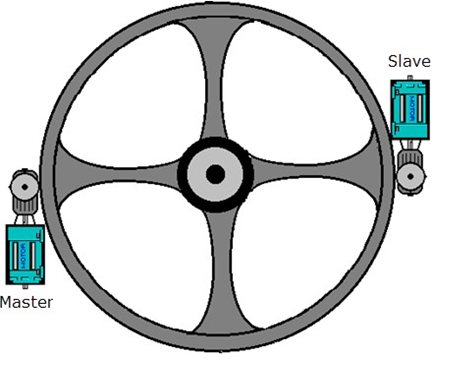
The example is based on a large diameter bull gear with two motors. The motors are coupled via tooth sprockets and gearboxes.
This creates a rigid connection between the motors, ideal for a torque follower setup.
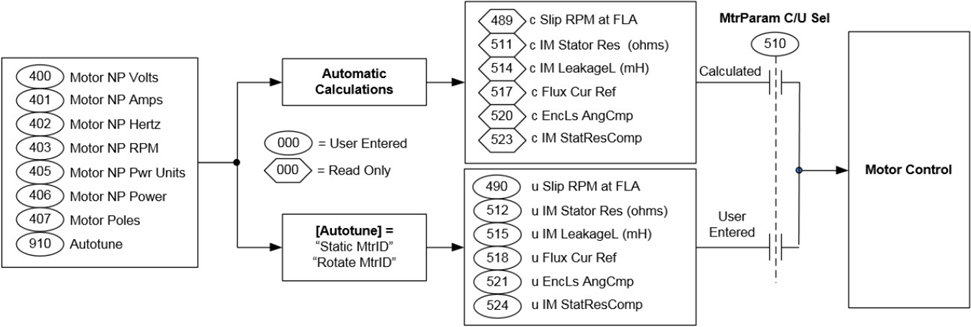
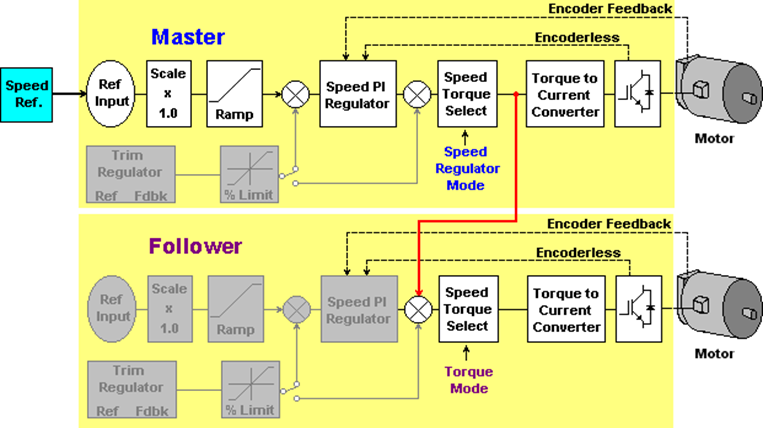
The torque follower (also known as master-slave) is a type of load sharing setup when we use one master drive in speed regulation and one follower drive in torque regulation.
The torque command generated by the master’s speed loop is transmitted to the follower drive to be used as torque reference.
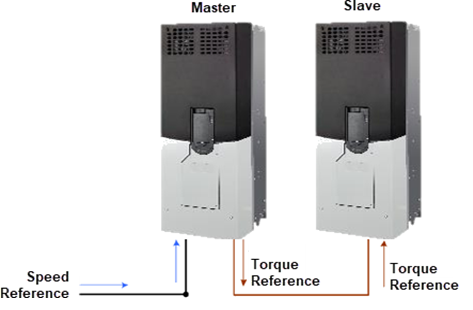
A torque follower setup makes two or more motors act as 1 big motor. See below torque follower block diagram.
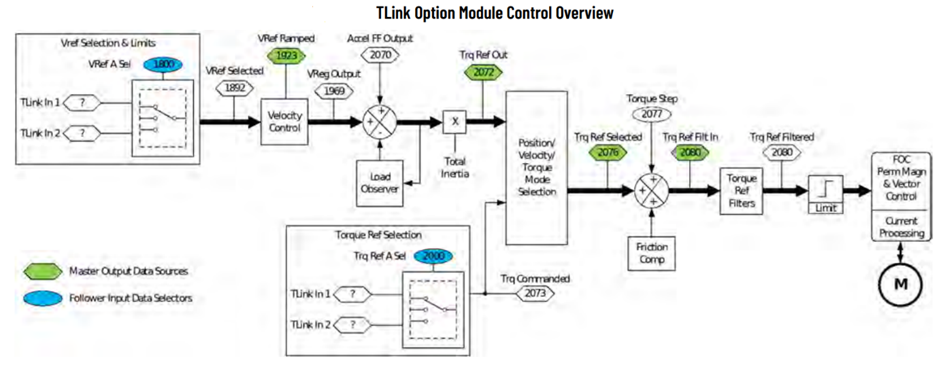
In this example the torque reference is transferred from the master drive to the follower drive via TLink option module.
Is this helpful?
If you are working with systems involving multiple motors coupled to a single load, this document will be very useful to you in setting up an efficient and effective control strategy.
How can I get this working?
- Hardware
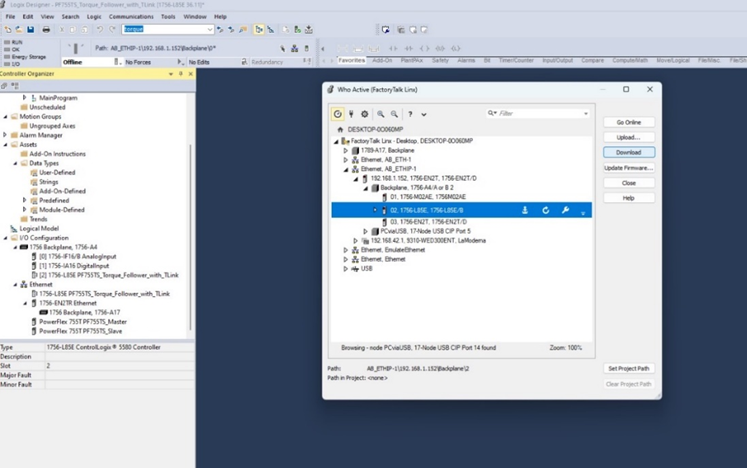
- Logix 5580-1756-L8SE Control
- PowerFlex 755T Flux Vector Tuning
- TLink (FO Module) - 20-750-TLINK-FOC-5
- Incremental Encoder Board 20-750-ENC-1
- Software
- Studio5000 (V36)
- Previous knowledge:
- Basic knowledge of Studio5000
- Basic knowledge of PowerFlex 755T.
References documents
- PowerFlex Drives with TotalFORCE control Quick Start, Rockwell Automation Publication 750-QS100D-EN-P - January 2023.
- PowerFlex Drives with TotalFORCE control Programming Manual, Rockwell Automation Publication 750-RM100C-EN-P - August 2022.
- PowerFlex 755T Flux Vector Tuning Application Technique, Rockwell Automation Publication 750-AT006D-EN-P - January 2022.
- TLink Option Module User Manual Original Instructions, Rockwell Automation Publication 750COM-UM100A-EN-P - June 2021.
Installation Guide
Application and Configuration of a Torque Follower System with PowerFlex 755T- and the use of the TLink Module (FO Module)
Version 1.0 - December 2024