- Using the software
- Ladder Editor
- Add-On Instructions
- Instructions
- Instruction set
- Code Editor Domain Specific Language Syntax
File Standard Deviation (STD)
The STD instruction calculates the standard deviation of a set of values in one dimension of the Array and stores the result in the Destination.
The standard deviation is calculated according to this formula:
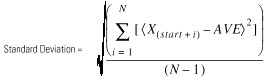
Where:
start = dimension-to-vary subscript of the array operand
xi = variable element in the array
N = number of specified elements in the array
AVE = 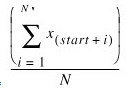
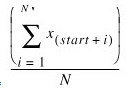
IMPORTANT:
Make sure the Length does not cause the instruction to exceed the specified Dimension to vary. If this happens, the Destination will be incorrect.
If an overflow occurs during expression evaluation or if the instructions reads past the end of an array, the instruction sets the ER bit and stops execution.
Available Languages
Ladder Diagram
_v1.png/_jcr_content/renditions/original)
Operands
There are data conversion rules for mixed data types within an instruction. See Data Conversion.
Ladder Diagram
Operand | Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Array | SINT INT DINT REAL | array tag | Find the standard deviation of the values in this array Specify the first element of the group of elements to use in calculating the standard deviation |
Dimension to vary | DINT | immediate (0, 1, 2) | Which dimension to use The order of the dimensions is: array[0,1,2] |
Destination | REAL | tag | Result of the operation |
Control | CONTROL | tag | Control structure for the operation |
Length | DINT | immediate | Number of elements of the array to use in calculating the standard deviation |
Position | DINT | immediate | Offset into the specified array which identifies the current element that the instruction is accessing.
Initial value is typically 0 |
CONTROL Structure
Mnemonic | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
.EN | BOOL | The enable bit indicates the STD instruction is enabled. |
.DN | BOOL | The done bit is set when the instruction has operated on the last element in the Array. |
.ER | BOOL | The error bit is set when the instruction generates an overflow. The instruction stops executing until the program clears the .ER bit. The .POS value stores the position of the element that caused the overflow. |
.LEN | DINT | The length word specifies the number of elements in the array on which the instruction operates. |
.POS | DINT | The position word is an offset into the specified array which identifies the current element that the instruction is accessing. |
Affects Math Status Flags
See Math status flags.
Major/Minor Faults
A major fault will occur if: | Fault type | Fault code |
|---|---|---|
.POS < 0 or .LEN < 0 | 4 | 21 |
Dimension to vary > number of dimensions | 4 | 20 |
See Common Attributes for operand-related faults.
Execution
Ladder Diagram
Condition / State | Action Taken |
|---|---|
Prescan | The .EN bit is cleared.
The .DN bit is cleared.
The .ER bit is cleared. |
Rung-condition-in is false | The .EN bit is cleared.
The .ER bit is cleared.
The .DN bit is cleared. The .POS value is cleared.
The rung-condition-out is false. |
Rung-condition-in is true | Internally, the instruction uses a FAL instruction to calculate the average: Expression = standard deviation calculation Mode = ALL |
Postscan | N/A. |
Examples
Example 1
Calculate the standard deviation of arrayDint, which is DINT[4,5].
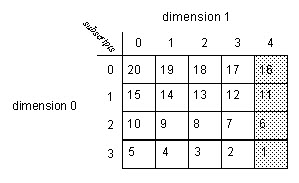
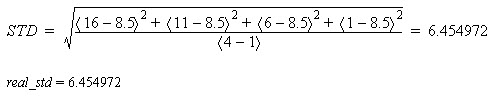
Ladder Diagram
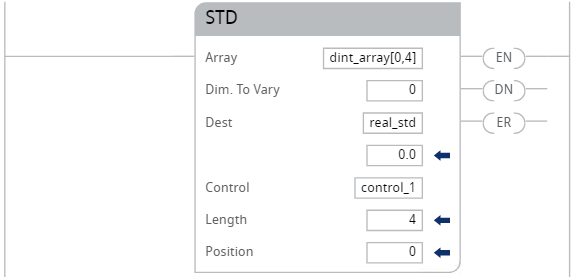
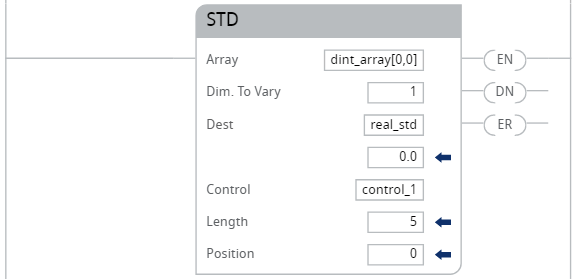
Example 2
Calculate the standard deviation of dint_array, which is DINT[4,5].
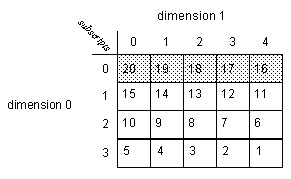
Ladder Diagram
Provide Feedback
